Applications of fluorescent peptide synthesis in molecular imaging
Synthesis of fluorescent peptides
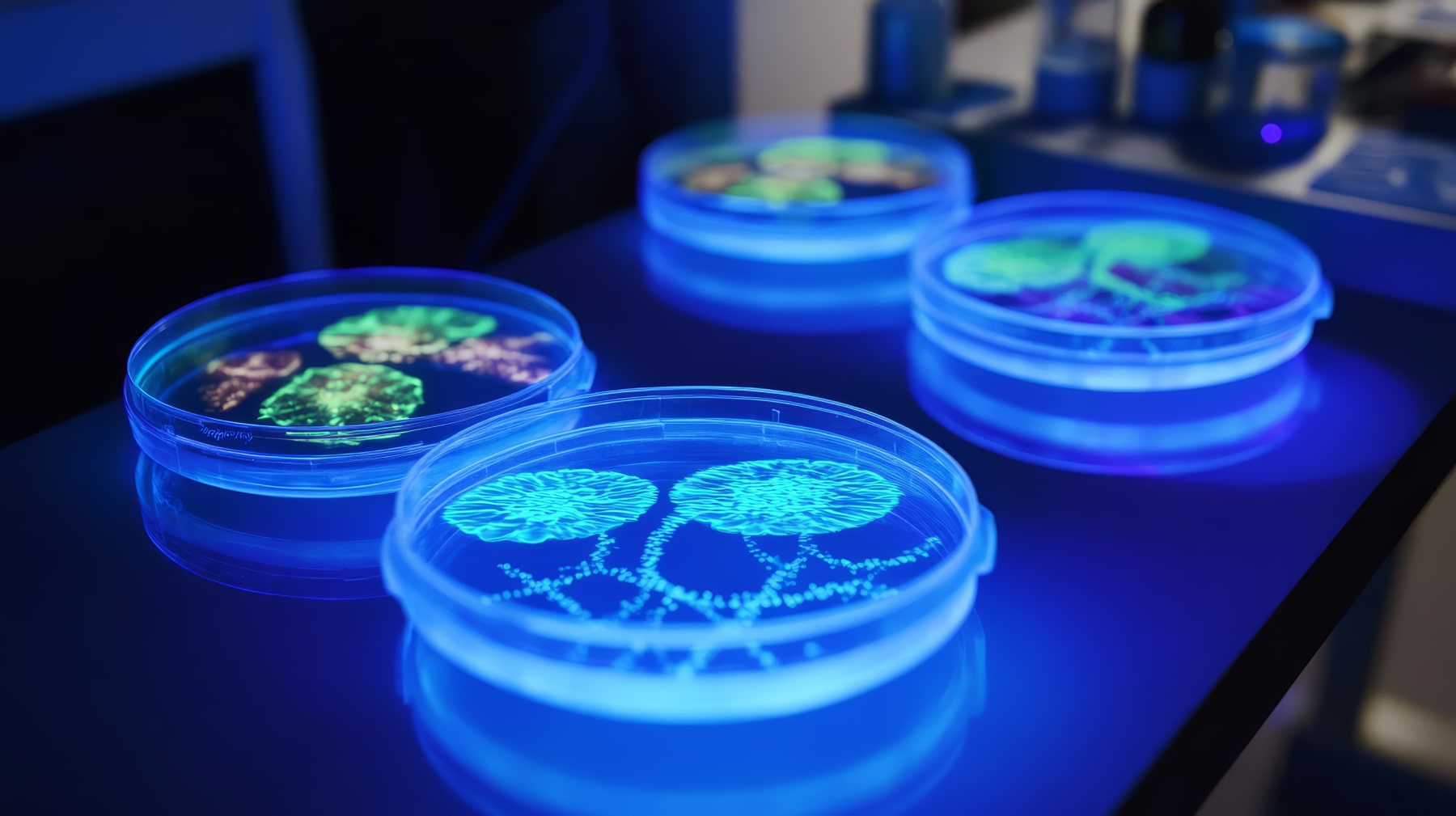
The synthesis of fluorescent peptides represents a technological breakthrough in biochemistry. It plays a crucial role in molecular imaging and involves the chemical coupling of amino acids to form peptide chains. Researchers attach a fluorescent probe to the amino acids before assembling them into peptides. This allows fluorescent peptides to specifically bind to target proteins when introduced into an organism or cellular solution.
These probes, thanks to their distinct optical properties, emit light when excited by certain electromagnetic radiation. These light signals are detected and quantified using specialized instruments such as confocal microscopes or advanced techniques like time-resolved emission. This enables the precise identification and localization of specific cellular structures with these fluorescent markers incorporated during the cellular biological cycle. Thus, the synthesis of fluorescent peptides is fundamental for deepening our understanding of various biological mechanisms such as protein interactions and intracellular signaling.
Molecular imaging
Advantages and diverse uses
The Role of fluorescent peptides in molecular imaging
The contribution of fluorescent peptides to molecular imaging relies on their unique ability to absorb and re-emit light, which allows for the specific labeling of biological structures. Their role is essential in:
- Tracking intracellular movement: Peptides can be used to visualize endocytosis or exocytosis pathways in real-time.
- Studying protein interactions: The unique optical properties of fluorophores enable examination of protein complexes within living cells.
- Detecting biomarkers: By specifically targeting certain molecules, they facilitate precise and rapid observation of biological processes.
- Experimental assessment: Longitudinal tracking of interactions can be achieved through non-invasive quantitative imaging with these light probes.
However, despite their undeniable advantages for high-resolution imaging without apparent tissue damage or notable side effects in vivo, several technical challenges still hinder their widespread use as ideal multimodal contrast agents.
Various types of applications
Scientific research
Cellular studies
Structural biology
Future developments
Technological perspectives
Innovative syntheses envisioned
Illustrative practical cases
Applications in studying biological processes
Multi-color fluorescent labeling
Maity, D. (2020). Selected peptide-based fluorescent probes for biological applications. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry, 16, pp. 1234-1256.
Zhang, Y., Ding, C., Li, C., Wang, X. (2021). Advances in fluorescent probes for detection and imaging of amyloid-β peptides in Alzheimer’s disease. Advances in Clinical Chemistry, 102, pp. 47-69.
Huang, Y., Chen, W., Chung, J., Yin, J., Yoon, J. (2021). Recent progress in fluorescent probes for bacteria. Chemical Society Reviews, 50(15), pp. 9432-9455.
Xiong, Y., Shi, C., Li, L., Tang, Y., Zhang, X., Liao, S. (2021). A review on recent advances in amino acid and peptide-based fluorescence and its potential applications. New Journal of Chemistry, 45(30), pp. 13557-13571.
Rodriguez-Rios, M., Megia-Fernandez, A. et al. (2022). Peptide probes for proteases–innovations and applications for monitoring proteolytic activity. Chemical Society Reviews, 51(2), pp. 467-488.
Scott, J.I., Deng, Q., Vendrell, M. (2021). Near-infrared fluorescent probes for the detection of cancer-associated proteases. ACS Chemical Biology, 16(9), pp. 1834-1844.
Duan, Q.J., Zhao, Z.Y., Zhang, Y.J., Fu, L., Yuan, Y.Y. (2023). Activatable fluorescent probes for real-time imaging-guided tumor therapy. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 178, pp. 113-134.
Minoshima, M., Reja, S.I., Hashimoto, R., Iijima, K. et al. (2024). Hybrid Small-Molecule/Protein Fluorescent Probes. Chemical Reviews, 124(5), pp. 678-699.
Liu, R., Xu, Y., Xu, K., Dai, Z. (2021). Current trends and key considerations in the clinical translation of targeted fluorescent probes for intraoperative navigation. Aggregate, 2(4), pp. 123-145.
Wang, Y., Xia, K., Wang, L., Wu, M., Sang, X., Wan, K. (2021). Peptide-engineered fluorescent nanomaterials: Structure design, function tailoring, and biomedical applications. Small, 17(20), pp. 2101234.


